News
- Application of DIN Rail Terminal Block for international marketDIN rail terminal blocks have a wide range of applications across various industries and are popular in the international market for their versatility, reliability, and ease of installation. Some common applications include: 1.Industrial Automation: DIN rail terminal blocks are extensively used in industrial automation systems for connecting sensors, actuators, switches, and other devices to control panels or PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). 2.Electrical Distribution: They are commonly employed in electrical distribution panels for organizing and distributing power and signals within buildings, factories, and infrastructure projects. 3.Renewable Energy: DIN rail terminal blocks play a vital role in renewable energy systems such as solar power and wind turbines, facilitating connections between inverters, batteries, and power distribution components. 4.Transportation: In the transportation sector, DIN rail terminal blocks are utilized in railways, ships, aircraft, and automotive applications for electrical connections, signal distribution, and control systems. 5.Building Automation: They are used in building automation and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems for wiring control devices, sensors, and actuators to manage lighting, temperature, and other building functions. 6.Telecom and Networking: DIN rail terminal blocks are employed in telecom and networking infrastructure for organizing and connecting cables, wires, and equipment in data centers, telecommunications cabinets, and networking enclosures. 7.Instrumentation and Control: They are integral to instrumentation and control systems across various industries, including manufacturing, oil and gas, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals, for wiring sensors, transmitters, and control devices. 8.Home Automation: With the growing popularity of smart home technology, DIN rail terminal blocks are used in home automation systems for connecting and controlling smart devices, lighting, security systems, and entertainment systems. 9.In summary, the international market for DIN rail terminal blocks is diverse and encompasses a wide range of industries and applications where reliable electrical connections and efficient wiring solutions are essential.
2024 04/03
- Market Analysis of Din Rail Terminal BlocksA market analysis of DIN rail terminal blocks involves examining various factors that influence the demand, supply, and overall market dynamics of these components. DIN rail terminal blocks are crucial components used in electrical and electronic systems for secure and organized wire connections. Here is a comprehensive market analysis of DIN rail terminal blocks: 1. Market Overview: DIN rail terminal blocks are integral parts of electrical and electronic systems across various industries, including industrial automation, power distribution, control panels, and more. They serve as a means of connecting and distributing electrical power and signals in a structured and efficient manner. 2. Market Drivers: a. Industrial Automation: The increasing adoption of automation in manufacturing and industrial processes is driving the demand for DIN rail terminal blocks, as they are essential for wiring control panels and connecting sensors, actuators, and other devices. b. Renewable Energy: The growth of the renewable energy sector, including solar and wind power generation, has led to increased use of DIN rail terminal blocks in power distribution and control systems. c. Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure projects, such as smart buildings and transportation systems, require reliable electrical connections, further boosting the demand for DIN rail terminal blocks. d. Data Centers: The expansion of data centers for cloud computing and data storage facilities relies on DIN rail terminal blocks for power distribution and networking. e. Electronics Manufacturing: The consumer electronics industry depends on these terminal blocks for efficient and compact wiring solutions in electronic devices and appliances. f. Energy Efficiency: The emphasis on energy-efficient solutions in various industries requires robust electrical connections, which DIN rail terminal blocks can provide. 3. Market Challenges: a. Competition: The market for DIN rail terminal blocks is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers and suppliers, making it challenging for individual companies to stand out. b. Cost Pressure: In price-sensitive industries, there may be pressure to reduce costs, which could affect the profit margins of manufacturers. c. Technological Advancements: As technology evolves, there is a constant need to innovate and provide terminal blocks with enhanced features, such as pluggable or high-current designs. d. Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to industry standards and regulations is essential, and companies need to invest in compliance testing and certification. 4. Market Segmentation: DIN rail terminal block market can be segmented by: a. Type: Terminal blocks come in various types, including feed-through, ground, fuse, disconnect, and more. b. End-User Industry: Segments can include industrial manufacturing, renewable energy, transportation, data centers, and more. c. Voltage Rating: Terminal blocks are available for various voltage ratings, and this can be a key segmentation factor. d. Region: Market dynamics may vary by region due to local demand, regulations, and economic factors. 5. Market Trends: a. Miniaturization: The trend towards smaller, more compact terminal blocks is driven by the need to save space in control panels and electronic devices. b. Pluggable Designs: Pluggable terminal blocks simplify maintenance and upgrades, making them popular in various applications. c. Industry 4.0: Smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives are increasing the demand for DIN rail terminal blocks with digital communication capabilities. 6. Competitive Landscape: Key players in the DIN rail terminal block market include Phoenix Contact, WAGO, Weidmüller, ABB, Schneider Electric, Eaton, and others. The market is competitive, with companies focusing on innovation, product quality, and customization to gain a competitive edge. 7. Future Outlook: The market for DIN rail terminal blocks is expected to continue growing, driven by technological advancements, increasing automation, and the expansion of renewable energy sources. Additionally, the push for more energy-efficient solutions and the development of smart infrastructure will contribute to sustained demand for these critical electrical components. It's important to note that market conditions may vary by region and industry, so a detailed analysis should consider specific market factors relevant to the target market and application.
2023 10/28
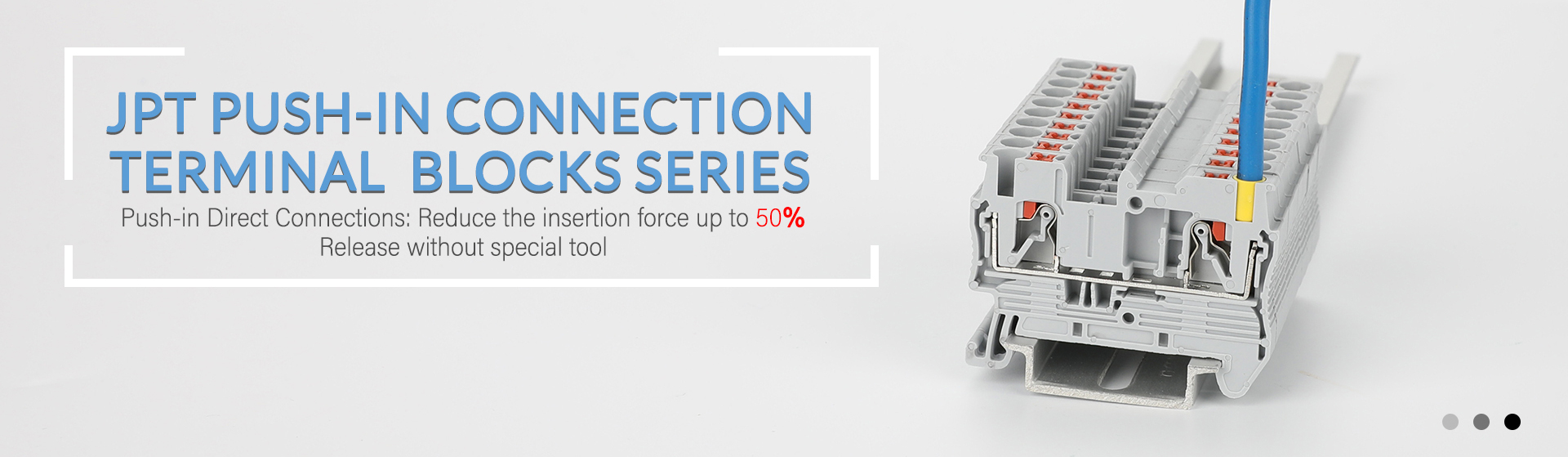
- Advantage of Push in distribution blocksPush-in distribution blocks, also known as push-in terminal blocks, offer several advantages compared to traditional screw-type terminal blocks. These advantages make them a popular choice in many electrical and electronic applications. Here are some of the key advantages of push-in distribution blocks: Ease of Installation: The push-in design eliminates the need for a screwdriver or any tool for wire termination. This feature simplifies and speeds up the installation process, reducing labor costs and saving time. Quick and Secure Connection: Push-in terminal blocks allow for fast and secure wire connections. The push-in mechanism securely grips the wire without the need for tightening screws, reducing the risk of loose connections or improper torque settings. Vibration Resistance: Push-in blocks are known for their excellent vibration resistance. The push-in connection method minimizes the risk of wires coming loose due to vibrations, making them suitable for applications in rugged environments and industries such as transportation and machinery. Space-Saving Design: Push-in distribution blocks often have a compact and low-profile design. This space-saving feature is valuable in applications with limited space within electrical enclosures or control panels. Reduced Risk of Over-Tightening: Traditional screw-type terminal blocks are susceptible to over-tightening, which can damage the wire or lead to unreliable connections. Push-in blocks eliminate this issue by providing a consistent and reliable connection without the need for manual torque adjustments. Tool-Free Maintenance: In addition to tool-free installation, push-in blocks also facilitate tool-free maintenance. Wires can be easily removed or replaced without requiring specialized tools, further reducing downtime during maintenance or repairs. Higher Wiring Density: Push-in blocks allow for a higher wiring density since they do not require screw heads or nuts. This can be advantageous in applications with a large number of wires or limited space. Reduced Risk of Short Circuits: The push-in mechanism often provides greater isolation between adjacent conductors, reducing the risk of short circuits due to accidental contact between wires. Suitable for Various Wire Types: Push-in distribution blocks can accommodate a wide range of wire types, including solid, stranded, and ferruled wires, providing flexibility in wire termination. Reliability: Push-in distribution blocks are designed to provide reliable, long-lasting connections. They are tested and certified for various standards, ensuring the safety and performance of the electrical installation. It's important to note that while push-in distribution blocks offer numerous advantages, the choice between push-in and screw-type terminal blocks should be based on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as the wire type, environmental conditions, and industry standards. Each type of terminal block has its own set of benefits and limitations, and the selection should be made considering the unique needs of the project.
2023 10/28
- Purpose and function of fan filterPurpose and function of fan filter The purpose and function of a fan filter are essential in various industries and applications where maintaining clean and controlled airflow is critical. Here's a breakdown of the key aspects of fan filters: Purpose: Dust and Contaminant Control: The primary purpose of a fan filter is to prevent dust, dirt, debris, and other contaminants from entering electronic equipment or systems. These contaminants can accumulate on sensitive components, impairing their performance and potentially causing damage. Environmental Protection: Fan filters serve to protect equipment from environmental factors such as moisture, humidity, and even small insects. In outdoor or industrial settings, these factors can be particularly detrimental to the proper functioning of electronic devices. Air Quality Improvement: In some applications, fan filters also contribute to improving air quality. By trapping particles like dust and allergens, they help maintain a cleaner and healthier environment for both equipment and personnel. Function: Airflow Regulation: Fan filters are strategically placed in ventilation systems to regulate the airflow. They ensure that air enters or exits the equipment in a controlled manner, preventing turbulent air and optimizing cooling efficiency. Contaminant Filtration: Fan filters are equipped with filter media (such as mesh, foam, or fabric) designed to capture particles as air passes through. These filters are replaceable, and their effectiveness depends on the filter material's pore size and quality. Protection of Equipment: The primary function of a fan filter is to protect the internal components of electronic equipment from contaminants. By blocking dust, debris, and other particles, they extend the lifespan of equipment and reduce the need for frequent cleaning or maintenance. Preventing Overheating: In electronic devices that rely on fans for cooling, like computers and servers, fan filters are crucial for preventing overheating. Accumulated dust can clog fan blades and obstruct airflow, causing the device to overheat, which can lead to performance issues or even hardware failure. Fan filters keep the cooling system operating efficiently. Maintaining Air Quality: In some cases, such as air purification systems or air handling units in HVAC systems, fan filters play a role in maintaining air quality. They capture airborne contaminants and allergens, contributing to healthier indoor environments. Enhancing Safety: In certain industrial applications where equipment operates in hazardous environments, fan filters can protect the internal components from exposure to potentially harmful substances, ensuring the safety and reliability of the equipment. In summary, fan filters are essential components in many industries and applications. Their purpose is to safeguard electronic equipment by controlling airflow, filtering out contaminants, and maintaining optimal operating conditions. Whether it's in electronics, HVAC systems, or industrial machinery, fan filters contribute to equipment longevity, performance efficiency, and improved air quality.
2023 09/02
- Common problems and solutions in the use of terminal blocksTerminal blocks are widely used in electrical and electronic applications to facilitate the connection of wires and components. However, there can be several common problems that arise when using terminal blocks, along with their solutions: 1. Poor Connection or Loose Wires: Problem: Wires may not be securely connected, leading to poor conductivity or intermittent connections. Solution: Ensure that wires are stripped to the appropriate length and inserted fully into the terminal. Tighten the screws or clamps properly to secure the wires in place. Use proper crimping tools for better wire termination. 2. Over-Tightening Screws: Problem: Over-tightening screws can damage wires, deform the terminal, or even break the screw or the terminal. Solution: Follow manufacturer guidelines for recommended torque values. Use torque screwdrivers or wrenches to avoid excessive force. Use terminal blocks with torque-limiting features if possible. 3. Incorrect Wire Sizing: Problem: Using wires with sizes that are too large or too small for the terminal can lead to poor connections or difficulty in fitting. Solution: Choose the appropriate terminal block size and wire gauge according to the application's requirements. Follow manufacturer guidelines for wire size compatibility. 4. Incorrect Wire Stripping: Problem: Improperly stripped wires can lead to poor connections or exposed conductors that might cause short circuits. Solution: Use wire stripping tools to remove the appropriate amount of insulation without damaging the conductor. Ensure that the exposed conductor fits properly within the terminal. 5. Misalignment of Terminals: Problem: Terminals might not align properly due to manufacturing defects or improper installation, causing connection issues. Solution: Inspect the terminal block for proper alignment before use. If misalignment is detected, replace the terminal block or adjust its position as needed. 6. Insufficient Insulation: Problem: Inadequate insulation between adjacent terminals can result in short circuits. Solution: Use terminal blocks with adequate spacing and insulation barriers between terminals. Avoid overcrowding the terminal block. 7. Vibration and Mechanical Stress: Problem: In applications subject to vibration or mechanical stress, wires might loosen over time. Solution: Choose terminal blocks with vibration-resistant features, such as spring-loaded terminals or locking mechanisms. Regularly inspect and tighten connections in high-vibration environments. 8. Environmental Factors: Problem: Dust, moisture, corrosive substances, and extreme temperatures can affect terminal block performance. Solution: Select terminal blocks with appropriate IP ratings for the environment. Consider using sealed or protected terminal blocks for harsh conditions. 9. Lack of Proper Labeling: Problem: Unclear or absent labeling can lead to confusion during installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting. Solution: Label each terminal with relevant information like wire identification, function, or connection points. This aids in easy identification and reduces errors. 10. Inadequate Testing: Problem: Not testing connections after installation can lead to undiscovered issues. Solution: After installation, perform thorough continuity and resistance testing to ensure proper connections. Remember, following manufacturer guidelines, industry standards, and best practices is crucial for avoiding these common problems and ensuring the effective use of terminal blocks.
2023 08/26
- Advantages of flame retardant PA66 material and disadvantages of non-flame retardant PA66 material for terminal block1.)Advantages of Flame Retardant PA66 Material for Terminal Blocks: 1.Fire Safety: Flame retardant PA66 (Polyamide 66) material significantly reduces the risk of ignition and propagation of flames. This is particularly important for terminal blocks used in electrical and electronic applications, as they are often located in environments where fire safety is critical. 2.Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have stringent safety regulations and standards that require the use of flame-retardant materials in certain applications. Using flame retardant PA66 material ensures compliance with these regulations. 3.Reduced Fire Spread: Flame retardant materials help contain and limit the spread of fire, which can be crucial in preventing larger fires or catastrophic failures in equipment. 4.Protection of Equipment: Terminal blocks often handle electrical connections, which can generate heat. Flame retardant materials provide an added layer of protection against heat-related issues and potential fires. 5.Enhanced Reliability: Flame retardant materials are engineered to withstand higher temperatures and adverse conditions without compromising their properties, contributing to the overall reliability of terminal blocks. 2.)Disadvantages of Non-Flame Retardant PA66 Material for Terminal Blocks: 1. Fire Hazard: Non-flame retardant PA66 material can pose a significant fire hazard, especially in applications where electrical connections are present. In the event of a fault or overheating, the material can contribute to the rapid spread of flames. 2. Regulatory Non-Compliance: Industries that require flame retardant materials for safety reasons may not approve the use of non-flame retardant PA66 in certain applications, leading to regulatory non-compliance and potential legal issues. 3. Limited Fire Protection: Non-flame retardant materials lack the ability to inhibit or delay the ignition and spread of fire. This can lead to increased risks to personnel, equipment, and infrastructure. 4. Reduced Safety Margin: In critical applications, a reduced safety margin due to the absence of flame retardancy can result in a higher likelihood of fire-related accidents or equipment failures. 5. Negative Environmental Impact: Non-flame retardant materials might not meet environmental standards, as they could release toxic fumes or contribute to pollution in the event of a fire. Shorter Lifespan: Non-flame retardant materials might degrade faster when exposed to heat and flames, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan for the terminal block and related equipment. In summary, the advantages of using flame retardant PA66 material for terminal blocks primarily revolve around fire safety, compliance with regulations, and improved reliability. On the other hand, the disadvantages of non-flame retardant PA66 material emphasize the increased fire hazard, regulatory non-compliance, and potential risks associated with its use in critical applications. When choosing materials for terminal blocks, especially in safety-critical environments, it's crucial to prioritize flame retardancy to ensure the protection of personnel, equipment, and infrastructure. Therefore, the plastic materials of all terminal blocks from Wonke Electric Co., Ltd. are flame retardant PA66.
2023 08/19
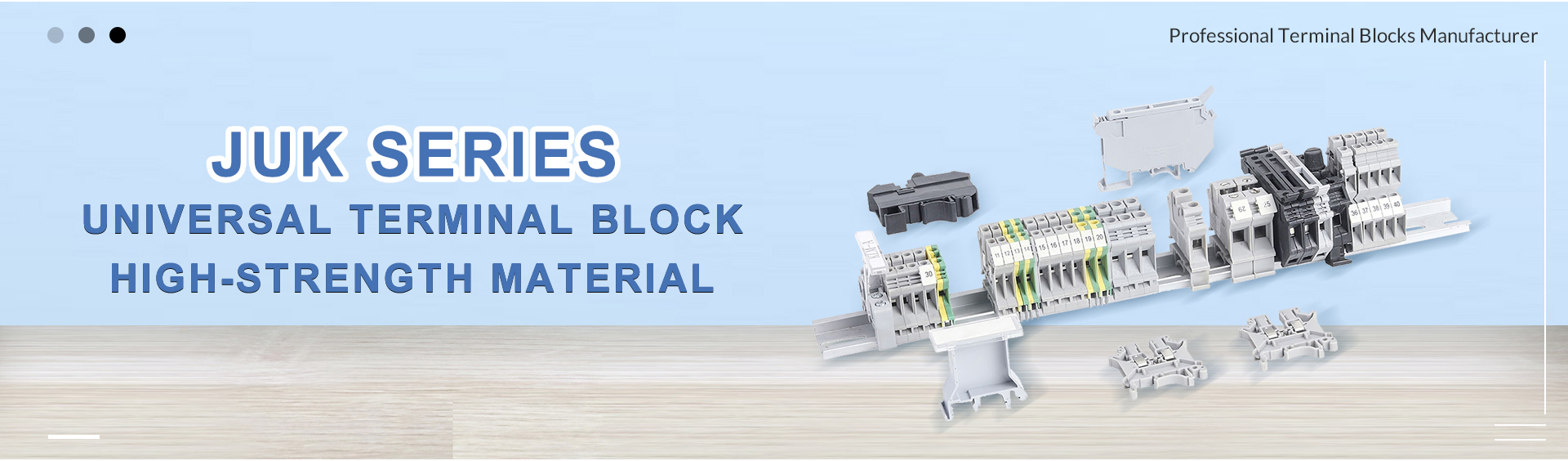
- Universal type of din rail terminal blocks and insulating materialsWith the increasingly frequent use of terminal products in the field of wiring, more and more users have put forward more requirements for them. For this reason, the structure and wiring methods of terminals have undergone great changes. From the initial single structure change, a variety of wiring structures are extended, which are classified into categories and suitable for various wiring environments, which greatly facilitates our use. At the same time, the structure of the terminal block is becoming more and more user-friendly, and the wiring speed is also greatly improved, which reduces the labor intensity of workers. At the same time, the reliability of the terminal blocks is getting higher and higher, the new production process and technical equipment are put into use, and the scientific production process and quality control methods have greatly improved the quality and life of the terminal blocks. With the increasing calls for environmental protection, the environmental protection requirements of terminals are very necessary. Halogen-free addition of flame retardants, non-toxic conductor insulators, and lead-free plating are all positive responses to this requirement. 1. Screw terminal blocks: Screw connection terminal blocks have always occupied an important position in the electronics industry, and now they have become an important component in the power industry. Its structural design takes into account the characteristics of convenient wiring and reliable screw connection. 2. Spring-Cage terminal blocks There are two types of connection methods for spring terminal blocks: pull-back spring connection and butterfly spring connection. Among them, the pull-back spring terminals and the screw terminals are compatible with each other, which greatly increases the flexibility. Reliable connection: front connection, connection is obvious, low maintenance, no tightening required. 3. Push in terminal blocks: Rigid wires or flexible wires with ferrules are directly inserted into the wiring position, which is convenient and quick. The contact spring opens automatically, creating sufficient pressing force on the current bar. When installing thin conductors with a wire diameter of 0.14 mm² or more, use a standard screwdriver to unscrew the contact spring. Compared with screw terminal blocks, it reduces installation time and insertion force by 50%, and can be wired without tools. In-line connection is a safe, reliable, simple and fast wiring method 4. Terminal Block Insulator Material Material nylon (PA66), flame retardant grade V0, and does not contain any harmful halogens, excellent flame retardant performance, safety, and environmental protection. Other commonly used materials include thermoplastic polyester (PBT); and liquid crystal polymer (LCP) used for perforation reflow technology The plastic insulating material and conductive parts of the terminal are directly related to the quality of the terminal, and they determine the insulation performance and conductivity of the terminal respectively. Failure of any terminal will lead to failure of the entire system engineering. The painful lessons that have happened at home and abroad in this regard are very profound.
2023 07/24
- Advantages of multi level terminal blocksMulti-level terminal blocks offer several advantages compared to standard single-level terminal blocks. Some of the key advantages include: 1.Space-saving: Multi-level terminal blocks allow for the termination of multiple conductors in a single compact block. This can significantly reduce the amount of space required for wiring connections, making them ideal for applications with limited space or dense wiring requirements. 2.Enhanced organization: With multiple levels or tiers, it becomes easier to organize and manage complex wiring configurations. Each level can represent a different circuit or connection, leading to a more structured and organized wiring system. 3.Reduced wiring errors: Multi-level terminal blocks often come with color-coded or numbered levels, which can help reduce the chances of wiring errors during installation and maintenance. This feature simplifies troubleshooting and makes it easier to identify specific connections. 4.Time-saving installation: The clear organization and labeling of multi-level terminal blocks simplify the installation process, as it becomes more straightforward to identify and connect the right conductors to the corresponding terminals. 5.Improved airflow and cooling: In applications where airflow and cooling are critical, multi-level terminal blocks can provide better ventilation due to their compact design. This can help in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for electrical components. 6.Flexibility and modularity: Multi-level terminal blocks often allow for modular configurations, enabling easy expansion or modification of the wiring system as requirements change. This feature enhances the flexibility and adaptability of the overall electrical installation. 7.Reduced maintenance downtime: Thanks to the organized layout and clear identification, maintenance and troubleshooting activities can be carried out more efficiently, reducing downtime and improving overall system reliability. 8.Safety and reliability: Multi-level terminal blocks are designed to ensure secure connections and prevent accidental contact or short circuits. They comply with industry safety standards, providing peace of mind regarding the reliability and safety of the wiring system. 9.Higher terminal density: Multi-level terminal blocks can accommodate a higher number of connections in a smaller space, making them suitable for applications with a large number of conductors to be terminated. 10.Potential cost savings: While multi-level terminal blocks may have a higher upfront cost compared to standard blocks, their space-saving capabilities and other advantages can lead to overall cost savings in terms of reduced installation time, maintenance efforts, and the need for additional wiring infrastructure. Overall, multi-level terminal blocks are a versatile and efficient solution for complex wiring applications, providing benefits in terms of space utilization, organization, safety, and ease of installation and maintenance.
2023 07/24
- What Does a Terminal Block Do?What Does a Terminal Block Do? There are multiple kinds of terminal blocks, including: · Ground terminal blocks · Fused connection terminals · Thermocouple terminal blocks · I/O blocks · Disconnect terminal blocks · Power distribution blocks While each specific block type may be used in a different context, they all provide the same function of connecting electrical components in a safe, reliable manner. Screw, spring, and push-in clamping options are available depending on a user`s needs for wire or conductor sizes. Once the wires are properly arranged within a terminal block, current will be able to flow between the incoming and outgoing sources. Terminal blocks work by directing electrical current through an insulated body, allowing for multiple wires to work simultaneously side by side. Are terminal blocks safe? It may seem like having so much power running through one source may be dangerous, but terminal blocks are specifically designed to route electricity in a manageable pattern. They are made of non-conductive materials such as plastic to minimize risk, and come in a large range of shapes and sizes to meet different project needs. When choosing a terminal block, you`ll need to consider its: · Current requirement · Voltage requirement · Wire compatibility · Environmental surroundings While it is possible to connect two wires together without a terminal block, connecting more than two can be challenging and dangerous. Once wires are stripped, the clamping element within the block keeps the lines securely in place, allowing the user to easily determine where everything needs to go. The insulated frame that houses the wires keeps the wires secure, and creates simple mounting for ongoing electrical projects. Terminal blocks tend to have high current and voltage ratings, and are much tougher than standard connectors. Because of their rugged, touch-safe design, blocks provide a versatility and reliability that lends their use to a wide variety of uses and industries.
2023 04/08
- Terminal Blocks - These Electrical Terminal Blocks cut down on short circuits.Terminal Blocks - These Electrical Terminal Blocks cut down on short circuits. Terminal Blocks features include: · Touch proof recessed screws and tubular contacts on these electrical terminal blocks provide added safety and helps prevent short circuits · Tubular contacts connect stripped, un-terminated solid or stranded wire directly to each contact · Integrated Stainless Steel spring wire protectors prevent twisting and breakage of stranded wire during termination · Modular 12-circuit design can be cut into smaller sections or stacked end-to-end · Dead front design to prevent shorts · Rugged Nylon 66 housing, UL 94V2 · Operating temperature rated at 230°F(110°C) · Brass Metal Alloy, Nickel Plated Terminal Insert · Can be used for AC & DC applications · Dimension Measurements = Inches · (Header Card Pack) Order Qty of 1 = 1 Header Card Pack of 2
2023 04/08
- How to select a terminal blockHow to select a terminal block Terminal blocks are common connectors that are intended to safely and effectively bridge the gap between two different circuits. Since they typically have power delivered from a larger source that is carried by wire conductors, terminal blocks are commonly found on industrial and power management electronic devices, such as variable frequency drives, motor protection relays, power and energy meters, power supplies and converters, HVAC and traffic controls, programmable logic controllers and many others. Power is most commonly delivered by wire, so it is always an option to land these wires directly to the assembly without costly adapters that only conform to certain products. Electricians and other installers can quickly work with this simple form of equipment installation and electrical integration. WKDQ offers feed-through terminal blocks and/or barrier strips that expect wire to have the conductive path managed through the housing in the rear of the block. There are varying voltage ratings and current ratings within the portfolio. This document will review wire feed through terminal blocks, different components, common terms, synonyms and items to consider when selecting a terminal block to integrate into your device or system.
2023 04/08
- Why Use Terminal Blocks?Why Use Terminal Blocks? Well-. you might ask, If you want to connect wires, why not just solder them together? Or twist them together and wrap them with electrical tape? Using terminal blocks is a much better solution for connecting wires. Terminal blocks provide more flexibility. For example, when using terminal blocks, wiring modifications are easy because wires can be removed or added quickly. Terminal Block wiring is neat and orderly allowing for quick identification making modification and troubleshooting easier. We`ll show you more good reasons to use terminal blocks later in this article. What are electrical terminals used for? Electrical Terminals are a class of electrical connector which are used to transfer electrical current from a power or grounding source to a use. Terminals "terminate" by crimping or soldering to wire or cable. Is a terminal block necessary? Terminal blocks increase safety by grounding, isolating, and protecting the other components in the electrical circuit. Terminal blocks are available with finger-safe connections to prevent electrical shock. And, terminal blocks can also provide test points, which add even more safety to the circuit. How do you select a terminal block? A good rule of thumb is to select a terminal block that has a current rating of at least 150% of the system's expected maximum current. The voltage rating should also be greater than the maximum system voltage. When thinking about this, voltage surges must be taken into consideration to prevent damaging the connection. What is terminal block in control panel? Terminal blocks were originally referred to as screw terminals because a screw was used to secure wires to a conducting plate, making an electrical connection. In control systems, terminal blocks are used to connect panel-mounted equipment to power and field wiring.
2022 08/20
- How To Choose A Terminal BlockHow To Choose A Terminal Block Choosing a Electrical Terminal Blocks is a simple, step-by-step process, and depends mostly on its application use case. You will need to consider such details as termination type, contact specs, orientation, mounting, and special features. The best practice method is to follow these four steps: Step 1: Select the type Step 2: Determine the electrical specifications Step 3: Select the accessories Step 4: Calculate the rail length STEP 1: SELECT THE TYPE We have already looked at some types of terminal blocks that are available. Now you will need to determine what type is required for your designated system, e.g. screw-mounted or screw-less, single feed-through or multi-level, fuse holder, ground circuit, direct mount, or disconnect. STEP 2: DETERMINE THE ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS Next, you should determine the electrical specifications required for each terminal block, which will include maximum wire size, voltage, and current. Wire entry sizes are usually quoted in mm² and determined by their amperage ratings. The size also depends on whether the conductor being used is solid or stranded, and also what range of conductor sizes may be included during field wiring. STEP 3: SELECT THE ACCESSORIES Once you have chosen between a deep or shallow block housing, then you can add the appropriate end brackets and block cover(s). You may also wish to use angled support brackets, top covers, separators, internal jumpers, test plugs, and printed or blank marking tags. Terminal blocks may also include one or more special features, such as circuit breakers, indicator lights. and lamp testing diodes. Pluggable terminal blocks are typically DIN rail mounted and can be stacked together to save space. Such blocks combine the terminals in a way that allows the power to be disconnected from the whole stack by removing one single plug. STEP 4: CALCULATE THE RAIL LENGTH To determine the length of DIN rail you will need in your assembly, you must calculate the total density per foot of all the different types of the terminal block and their respective quantities. Half an inch (½") must then be added for each rail end to accommodate the required rail mounting screws, plus 0.0008" (0.2 mm) additional tolerance per terminal. For the calculation to be complete, you must also add the width of the end covers, the end brackets, and any separators.
2022 08/19
- UKK power distribution blocksUKK power distribution blocks make safe connections even in tight spaces In expanding its commitment to providing standard duty connections, Wonke Electric is proud to announce the addition of a new Power Distribution Block series to its selection of IP 20 feed-through terminals. These DIN rail/direct mountable blocks are intended for distributing main power sources for low voltage (690 V, 80-500A) applications, utilizing large wire sizes, and of course, maintaining finger-safe connections. Further, these distribution blocks allow for multi-pole assembly with built-in joiners to gang blocks together to generate two and three-phase groupings. Wonke UKK Series Power Distribution blocks are not your typical distribution blocks: they are clearly designed with the future in mind. They minimize installation costs by unifying power connections in the control cabinet to a single bus module instead of the always bulky and sometimes non-finger safe traditional barrier style blocks. Manage multiple load connections from one to nine poles. Line and Load connections are designed to grip a wide range of wire sizes (AWG 14 – 3/0) making inventory selection for numerous requirements a snap. With application flexibility, reduced installed cost, and safety included, the Wonke Power Distribution Blocks deliver power and performance. – Available in current ranges from 80A to 500 A at 690 V – IEC finger-safe design – PC and Vo Anti Flaming PA66, Brass – IP 20 – DIN rail or direct mount compatible Wonke Electric www.wonkecontact.com
2022 03/02
- Connectors: Basic Type of terminal blockWhile components are ever increasingly being integrated into single packages such as SOCS and single-board computers, it can be argued that one component type, connectors, will always be around. In this article, we will learn the basics of connectors, why choosing the right one is vital for any design and some common examples of terminal blocks. Introduction While electronic circuits can process signals and produce outputs, they almost always need to be connected to external components, power sources, inputs or outputs. These connections are done with the use of connectors, and they come in many different types, shapes, sizes and ratings. Choosing the wrong connector for your design can cause a range of issues, from bulky product sizes to components catching fire, so understanding the different types of connectors is imperative. And while there are many connector types available (pin headers, sockets, DIN and DB, for example), this article will focus on terminal blocks specifically, since they are found in just about every single sector, ranging from domestic wiring to industrial rack systems connecting to various I/O. Terminal blocks at a glance Terminal blocks are connectors that terminate a single wire and connect it to a circuit or other system. Terminal blocks come in a range of shapes, sizes and ratings, but always terminate a single wire (single pole) and are never multi-pole. Terminal blocks are available as rows, but each terminal connects to only a single wire. Terminal block connectors are very useful in situations that require semi-permanent connections, which may require inspections, wire replacement, repair and change (this is why terminal blocks are incredibly common in domestic wiring and industrial environments). While not all terminal blocks have PCB contact pads or legs, they always have some mechanically solid body made of plastic or other insulating material. The most common connection method for terminal blocks is the use of a screw, wherein wires are inserted and then clamped down with the use of a single screw. Larger terminal blocks used with large cables typically have the screw pushing the wire against a metal body, whereas terminal blocks used with thinner wire use a screw that pushes down on a lever or flat head that compresses the wire against a metal insert. Other terminal blocks may use screw-less levers, which can be thought of as a fish trap; the wire is inserted and the lever comes down, which prevents the wire from being pulled back out. Another terminal type are terminal blocks with screws for holding an inserted cable on one end and a plug on the other end so that the block can be inserted into a female connector (this allows for hot-swapping). Types of terminal blocks Screw terminals Screw terminal blocks are those that have a screw as the method for holding a cable or wire. It is more common to see screws have flat-head fittings, and these types of terminals are often found in situations in which voltage and current demands will be moderate (domestic/commercial wiring). While wires bound to a terminal block are not physically bonded with the use of solder, they are incredibly strong if done correctly and can be used in permanent scenarios. Great care should be taken when tightening terminal blocks because over-tightening can damage the inserted cable and result in an unreliable and potentially dangerous connection. Barrier Terminals Barrier terminals are very similar to screw terminals in that they use screws as the mechanism to hold cables. Barrier terminal blocks often have more than one termination point for multiple cables and, because of this, have small barriers between individual terminals. Barrier terminals can also have small lids and enclosures to further protect cabling and are commonly found in domestic wiring and other high-voltage scenarios that need to prevent arcing or potential short-circuits. Push-fit terminals Push-fit terminal blocks use small spring-loaded levers that allow cables to enter the terminal block in one direction but do not allow them to leave, effectively holding the wire in place; hence, the name [push-fit." This type of connector has some advantages over screw terminals in that they prevent over-tightening, but as a result, the designer is reliant on the spring having enough force to keep the wire in contact with the conductive body. Another issue with push-fit terminals is that some are not designed to be reused and lack a removing lever, which makes repair work difficult because whole terminals may need replacing. Pluggable terminals Pluggable terminal blocks are those that have a cable entry to allow the connection of a wire or cable but a plug output to allow for easy connection to a socket. These types of terminal blocks are very useful in situations in which hot-swapping may be important or a connection is expected to be removable for servicing or inspecting. Screw contacts are the most common type of connection method for inserted cables, but the screw often has a small metal plate attached to the end, which allows for gripping of both small and large cables. How to decide the terminal for you Choosing the right type of connector for your application may seem trivial but, in fact, is more complex than you may realize. The aspects of terminal blocks that need to be considered are typically current requirements, voltage requirements, wire being used, mechanical strength and the environment. Current requirement Current requirements are arguably the most important aspect to consider because pushing too much current through a terminal block can result in overheating and, therefore, the destruction of the terminal block. When looking for a terminal block, be sure that the chosen block can, in fact, handle the current that you expect to use plus 50 percent more. For example, if an expected current of 2 A is to be drawn from a block, then a terminal block with a current rating of 3 A would be sufficient. Voltage requirements Just like current draw, voltage also needs to be taken into account. Voltage causes problems with dielectric breakdown such that a voltage too high for a terminal block could cause current leakage between adjacent terminal blocks. However, high voltage requirements are often rare in design, which is why voltage considerations are typically ignored for voltages under 100 V. However, it is still important that this figure is checked before a terminal block is chosen! Wire being used Not all wires are equal, and each wire type has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, when choosing a terminal block for a cable, be sure to know the size of the cable (can it physically fit into the terminal block?) as well as if it`s single-core or multi-core. Multi-core wire does very well in screw terminals, whereas single-core wire does well in push-fit connectors. Environmental/mechanical strength The environment is a very important aspect to consider when choosing a terminal block. Some terminal blocks may be mechanically strong and able to handle high currents, but if the connection is being used in a naval environment, then the salty air could be detrimental to the metal contacts. The environment could also have wide temperate swings or contain mechanical vibrations, which make screw terminations unreliable. Conclusion Terminal blocks are used in many designs and choosing the right one is very important. Learning to recognize the different types of connectors and their advantages and disadvantages can save designers time and money by understanding what their product is, what it will experience and in what environment it will be used.
2021 06/11
- Advantages of WKDQ din rail terminal blocks in the energy, machinery and system manufacturing industriesApplications of Energy Industry Wonke Electric's terminal blocks have been used in the energy supply industry for decades. This is mainly due to the excellent electrical and mechanical characteristics of the product series. The materials used in Wonke Electric's terminal blocks can be protected from environmental influences and maintain long-term stability. So it has a very high quality. High-quality materials are the guarantee of long-term reliability. Applications of Machinery and System Manufacturing Wonke Electric's terminal system can provide compact, high-performance electrical connections. The product guarantees the long-term stability of the connection with its high-quality physical characteristics and advanced industry standards. The high quality of the product has been verified by domestic and foreign standard tests, ensuring the safe use of the terminal in the industrial field of machinery and system manufacturing. Wonke Electric provide combined terminal series, The user can choose the connection method arbitrarily according to actual needs. The available connection methods are as follows: JPT push in directly connection JST spring cage connection JSAK and JUK screw connection Whether direct push-in connection, spring clamp connection or a screw connection, the same bridging system is used, and each other can be bridged arbitrarily. The combined connection terminal blocks has great flexibility. The fully agreed bridging, marking and testing system can help customers select models, distribute goods, and reduce logistics costs. And all terminal blocks of Wonke Electric have passed CE, ROHS, CQC certification.
2021 06/08
- What`s there to know about terminal blocks for control applications?What`s a component that forms the backbone of most motion or automation control systems but that often times goes unacknowledged? We`re talking, of course, about the hard-working terminal block. What exactly is a terminal block and what function does it serve in motion/automation systems? The most basic definition is that it provides an electrical connection point for two or more wires. Terminal blocks were originally referred to as screw terminals because a screw was used to secure wires to a conducting plate, making an electrical connection. In control systems, terminal blocks are used to connect panel-mounted equipment to power and field wiring. A typical control cabinet showing pluggable terminal blocks mounted to DIN rails with wire connections labeled for easy identification. A typical automation system inside of an equipment rack may contain any number of components (such as controllers, PLCs, I/O modules, etc.) mounted on DIN rails and connected together via terminal blocks. Types of terminal blocks There are a large variety of terminal blocks for varying needs. General-purpose types are broadly usable in many applications as simple termination points to make electrical connections. Other examples include terminal blocks for I/O, for power distribution, as well as for motor connections, both single-phase and three-phase motors for various industrial uses. Other common types include ground blocks designed specifically for making a connection to ground and fuse blocks where two wires make a connection to a fuse, providing circuit protection. www.wonkecontact.com This single level terminal block from Automation Direct shows clearly the basic mechanism of the screw-type block. Wires are inserted on the side and make contact with a conducting bar and are secured in place with a screw tightened from the top. Another common way to classify terminal blocks is by the method of terminating the wire or making the connection. Terminal blocks are available with a number of different connection methods. The most common are screw-in types where the wire is pressed against a metallic conducting plate or bar and tightened down with a screw to secure it physically and make an electrical connection. Spring-loaded terminals use the force of a spring to maintain the connection of the wire to a conducting plate. There are also push-in terminal blocks where a wire attached to a ferrule is inserted into a hole in the block. Other types include insulation-displacement connectors (IDC) that don`t require the wire to be stripped prior to insertion into the terminal block. An example of a DIN-rail mountable terminal block. (Image via WKDQ) Other differentiating features may include the size of the terminal block, the number of possible connections, as well as voltage and current ratings. Typical examples can range from standard signal levels such as 1 to 5 V or 4-20 mA to power supply connections with high amperage current ratings and voltage ratings of hundreds of volts. Other important factors include the type of wire connections that can be terminated (i.e. stranded or solid wire) of different gages (AWG sizes), as well as the so-called levels, as in single (for a single wire-to-wire connection), double, or triple levels offering multiple connections on the same block.
2021 04/23
- How to Properly Use a Terminal BlockHow to Properly Use a Terminal Block A terminal block is one method of connecting a selection of different electrical wires. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes so you can normally find one that will be compatible with whatever project you are carrying out. However, the difference between blocks can lead to problems if an incorrect type is used or if it is not connected properly. Follow the advice below so you never have to worry about encountering these issues. Step 1 - Terminal Block Type Look at the electrical equipment you are working on to see what type of connection it requires; normally you will have either a screw-in or plug-in connection. Screw-in wires are placed inside the terminal block and screwed into position, and they are most common for equipment that does not require high voltage protection. A variation on the screw-in connection is one held in place by a spring mechanism. This connector can reduce the time spent on the job because you simply clip it into place instead of removing and replacing the screw. A plug-in connection has a male terminal at the end of the wire. This terminal is connected to the female port on the terminal block and forms a secure connection. Plug-in blocks are commonly used in the fuse boxes of automobiles. Step 2 - Choose Terminal Block Once you know the type of connection that is required, you need to find a terminal block that fits the rest of your requirements. Consider what space you have for the connection and how many wires need to be connected. Terminal blocks are supplied in a variety of shapes and sizes, so you should be able to find one that suits your needs. Next, choose the correct rating. Three, five, 15, or 30 Amp terminal blocks are widely available, and you'll want to buy the one that meets the highest current level it will conduct in order to allow the most powerful piece of equipment to function. Step 3 - Secure Screw-in Connection Always make sure that any electrical equipment is turned off before beginning work. For a screw-in connection, you will need to strip a small amount of the insulation from the end of the wire. Normally, around 1/2 inch is sufficient but this will depend on the component. Unscrew the retaining screw from the terminal block then insert the wire into the hole. Tighten the screw into place. Make sure it is fully tightened because if the wire is left loose, it will begin to heat up and melt the insulation. Over time, this could result in a fire so take a little extra time to make sure it is secure. Step 4 - Secure Plug-in Connection Position the terminal block and run the electrical wires to it, connecting the male terminal to the female port. Press firmly to ensure the connection is secure and won't come loose in the event of any subsequent movement. Step 5 - Test Equipment Once you have made all the connections to the terminal block, test your equipment to make sure it works correctly. Afterward, check the terminal block and the connections to make sure there is no excessive heat build-up and the wires are still securely in place.
2021 04/16
- Terminal blocks ensure safe currents as well as safe wiring of installationsFrom control panels for industrial productions to fuse boxes in private homes: Terminal blocks ensure safe currents as well as safe wiring of installations. Plastics used to manufacture terminal blocks have to meet high requirements for fire protection and mechanical and thermal properties. In electrical engineering, terminals are used to connect wires and cables. Continuous safe contact has to be ensured for the connection – mechanical fixing ensures this. Terminal blocks can be arranged in any order on a mounting rail and installed with a simple snap. This defines the mechanical properties required for this material: plastics used in this application must exhibit high elasticity and good toughness – or run the risk of breakage when snapping. Connections require sufficient stiffness and strength. When handling electrical power, sparking and fires may occur. Other requirements include high temperature resistance and heat aging resistance Plastics have electrical insulating properties, which generally recommends them for electronic applications. Terminals are produced in extremely large quantities by injection molding. Economic production requires short cycle times and low maintenance cost for injection molding tools and machinery. It is also necessary to be able to produce very low (0.4 mm) wall thicknesses with the plastic. In addition, good colorability of the material plays an important role: Different colors of the terminal blocks serve to differentiate between different functions (e.g. neutral conductor, protective conductor, etc.) and ensure safe installation. Due to the high requirements , PA66/6 copolyamid are especially suitable for the application in terminal blocks..The terminal block made from NYLON with V0 Flame retardant and the conductor is Copper with good conductive, stainless steel spring make the wire not easy fall down from the terminals.
2020 12/09
- Terminal blocks may use one of several different methods to achieve wire connection.crew clamps use a screw to tighten the wire and make an electrical connection and are the classic, industry standard termination method. This type can accommodate a very wide range of wire sizes and provides a reliable connection. Spring clamps use the force of a spring to retain wire clamping. They represent a newer alternative to screw clamps and are particularly useful in applications using small wire diameters and limited working space. Insulation displacement connections (IDC) push the wire between two sharp pieces of metal, allowing a connection to be made without exposing any bare wire. Tab connections are designed to be inserted and removed rapidly without the need for soldering. They are also known as spade or blade terminals. Orientation Terminal blocks are commonly available with one of three different wire entry angles: 45°, 90°, or 180°. 90° and 180° types are also referred to as horizontal and vertical, respectively. Contact and Wire Specifications When discussing terminal blocks, the term "contact", also known as a position, way, or pole, refers to a wire attached to the block. The number of contacts is an important specification when considering a product, as a buyer is required to match this number with the number of wires necessary for a project or application. Contact pitch refers to the distance between each contact, measuring from the center of each hole or opening. Contact pitch is directly related to the number of contacts and is typically expressed in millimeters (mm). Terminal blocks are typically manufactured to accept a range of wire or conductor sizes. North American wire size is expressed in American wire gauge (AWG), which is a standard for non-ferrous wire conductor sizes. Higher AWG numbers represent smaller conductor diameters, and vice versa. For example, a typical AWG 12 household wire has a larger diameter than a AWG 22 telephone wire. Features Terminal blocks may include one or several special features. The wire connections on pluggable terminal blocks allow for the circuit to be broken without any unwiring, enabling quick disconnection, testing, and maintenance. Pluggable terminal blocks can often be combined in such a manner that removing a single plug disconnects power to the entire group of terminals at once. Stackable terminal blocks can be mounted next to each other to save space; they are typically DIN rail mounted devices. The product may feature an indicator light, typically a light-emitting diode (LED), to verify that current is flowing through the device. Some terminal blocks feature a diode between circuits to allow lamp testing and provide reverse polarity protection.
2020 12/09
Email to this supplier